Architecture
LA Story: Architecture's Role In Solving The Affordability Crisis
As a context to explore inspired and inspiring concepts, LA's "Low Rise" competition winners hew to a central theme: architecture as a solution for social, policy, economic, and cultural challenge.

Image source: Vonn Weisenberger
The human toll of Los Angeles' housing affordability crisis numbs the mind in its enormity.
There are other tolls, too. Equally numbing in their statistical, no-way-out vastness. A 2019 McKinsey Global Institute analysis of LA's housing crisis estimated an order of magnitude – 1.9 million households across LA County – as a benchmark of those who "would have to stretch financially to obtain a standard-size unit in their current neighborhood." The study notes that while builders and developers produced upwards of 90,000 new homes in LA during the decade past, as few as 12% of those new homes gave access to housing for people earning below area median incomes.
These facts are not news. They have rattled in an echochamber for years, the risks, the exposure, the vulnerability, and the loss all fighting for meaning and matter as a sense of helplessness nudges toward complacency. The epitome of stagnation, the bane of dynamism.
Another measurable consequence of LA's housing affordability challenge comes in the form of a gut-punch to the City of Angels' very sense of itself as a place, its dynamism. McKinsey's analysts write:
We estimate that the shortage of affordable housing depresses GDP across the metro area by more than 2 percent. This translates into $18 billion to $22 billion in lost output every year for the City of LA, and almost double that amount for all of LA County. Most of this occurs as households forgo other types of consumption to pay the rent or mortgage. Consumption is limited even further for Angelenos who face high transportation costs because they cannot afford to live near their place of employment—a situation that contributes to some of the nation’s worst traffic congestion and related environmental consequences. The people who provide many of the services Los Angeles depends on every day are finding it harder to get by or to live anywhere near where they work.
McKinsey's illustration of what a solutions path looks like in terms of a confluence of forces is here:
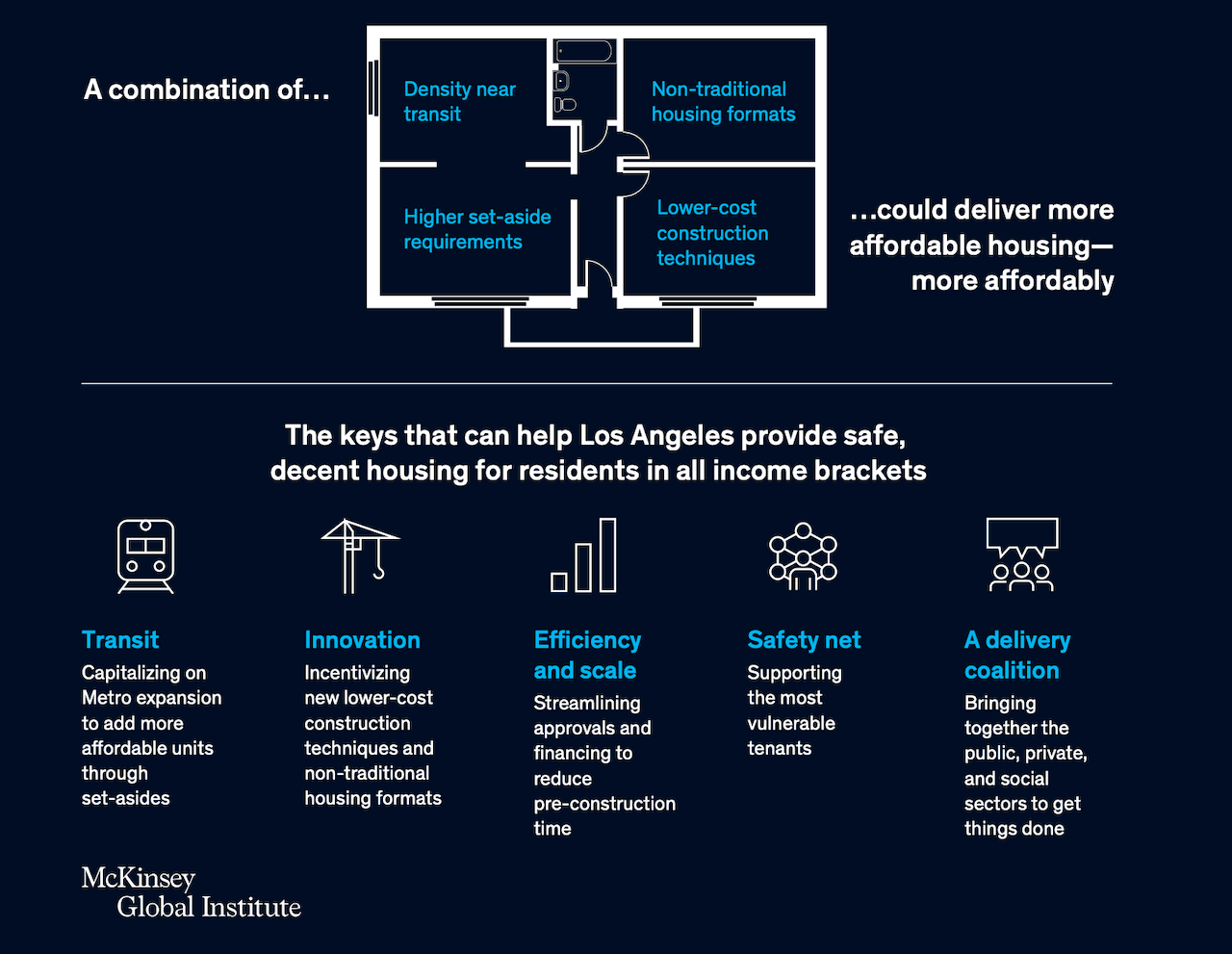
Crises, by their nature, define moments of passage where one of only two outcomes are possible: things get better or they get worse. There's no staying the same.
New York Times architecture critic Michael Kimmelman spotlights winners of LA's vaunted "Low Rise" architecture competition in light of an overarching gorilla-in-the-room question: "Can design help in solving LA's housing affordability crisis?"
Kimmelman phrases the challenge like this:
Can California’s biggest city — and possibly America’s least affordable one — redesign its way out of the housing crisis?
As a set-up context to explore inspired and inspiring architectural concepts, Kimmelman energizes the narrative's drama, whose plotline hews to a central theme: architecture as a solution for social, policy, economic, and cultural challenge. He writes:
The trajectory of housing in Los Angeles during the later years of the last century paralleled that of many other American cities where density came to be equated with urban decline and white residents resorted to redlining and other racially restrictive practices to keep out Black people and immigrants. Slow-growth policies, in Los Angeles’s case fueled especially by fears of Manhattanization, slammed on the brakes for multifamily housing construction. Single-family zoning became the norm. Leaning into its freeway system and an environmentally oblivious mythology of the desert as an endless terrain for exurban expansion, Los Angeles, by 2010, had shrunk its zoning envelope to 4.3 million people.
The power of architectural brilliance – captured in the "Low Rise" winning entrants' on-the-boards visions – figures as an essential role-player in housing as a solution across an array of societal inequities, unbalances, friction, ugliness.
Without architecture, no solution can possibly excite diverse and inevitably oppositional human interests to work together to expand healthy, decent, supportive housing access for more people soon.
Architecture by itself, however, can not be expected to tip the forces of money and power and control necessary to spark political will, move capital investment, bring win-win talent and resolve to a no-win, self-perpetuating cycle, whose superficial and fake debate poses environmental stewardship against access to decent homes and sustainable communities.
Design, probably like no other tool, sparks human beings' primal homing instinct. It belongs in the mix – as does transformative land-use policy and more-advanced construction technology, augmented by data that validates equity-bound capital investment – as a sine qua non capability.
To Kimmelman's question, can LA "redesign" its way out of the crushing throes of a housing crisis that threatens the great city's dynamism, we'd say yes.
But not if redesign means architecture alone. Redesigned policy, redesigned building technology models, redesigned capital investment models, redesigned public-private partnerships, redesigned social compacts, and redesigned precepts of justice go with the turf.
The possibility and potential of all that redesign can tap architects as a source of clarity of vision, of sustaining impetus, and of cohesion among disparate forces.
Gertrude Stein was referring to her childhood home in Oakland – not LA – with an iconic line. "There is no there there."
Redesign, in all its range of meanings, can more "there" there in LA.
Join the conversation
MORE IN Architecture
Design-Estimating Disconnects Cost Builders Time And Margin
Former builder-operators Brandon Pearson and Marcus Gonzalez share what’s broken—and how connected teams can win now and in 2030.
How Missing Middle Housing Wins Approval And Works
Architect and planner Dan Parolek coined the term “missing middle housing.” His firm’s projects prove that thoughtful design, political navigation, and local momentum can overcome entrenched zoning resistance.
Faster Builds, Better Margins: The ROI On Right-The-1st-Time Velocity
Inside the digital transformation of homebuilding: How integrated teams, shared data, and AI are turning velocity into a high-stakes profit advantage.
